
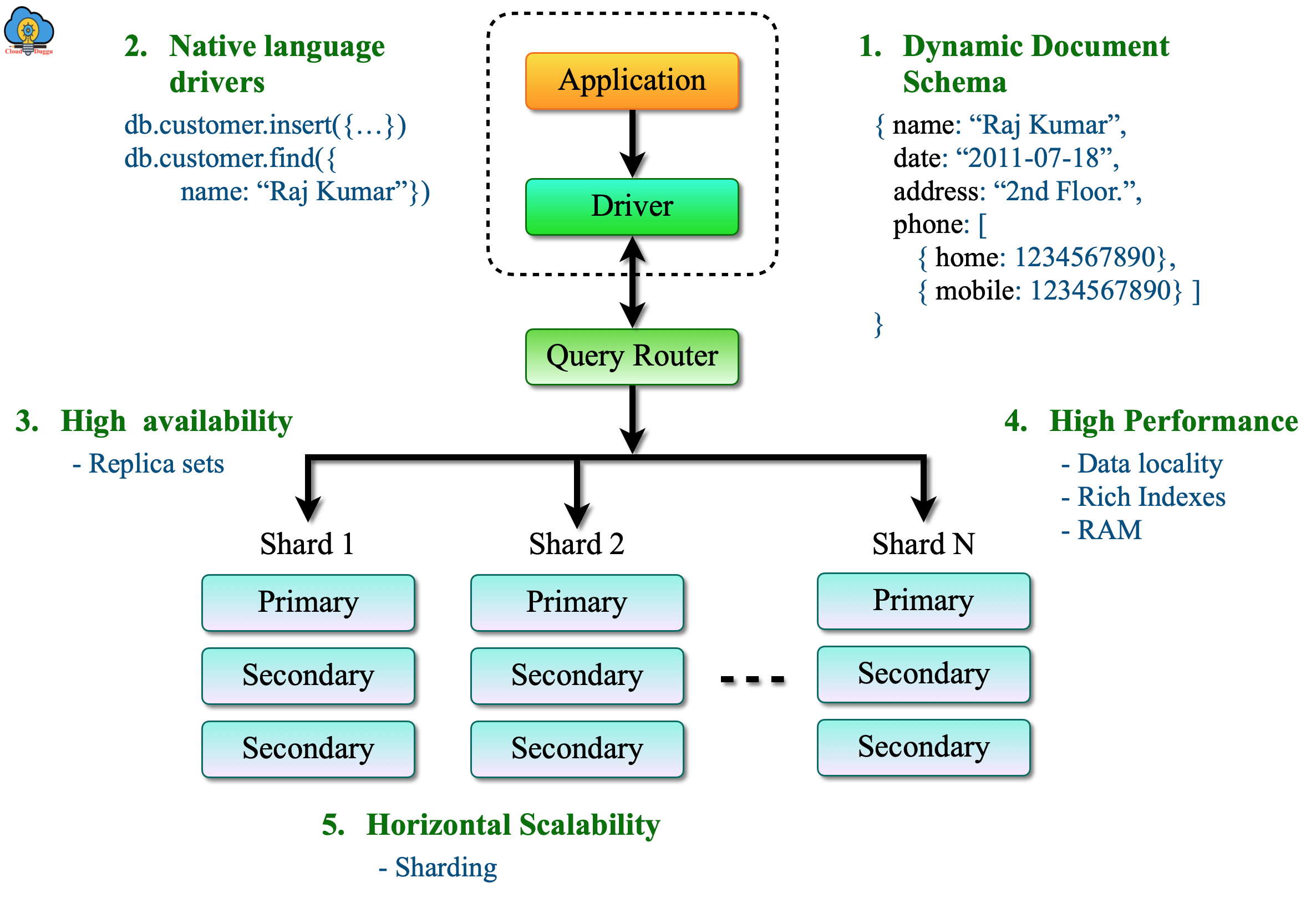
Grouping, sorting, limiting, and joining of data using $lookup and $graphLookup to another collection.Views are defined using the standard MongoDB query language and aggregation pipeline, and can use: Developers and DBAs can change the schema of the underlying collection without affecting the applications that use the view. By restricting access to sensitive data, data can be partitioned to reflect different access rights, without creating separate silos.Īdditionally, views can show calculated fields without exposing underlying customer data or affecting the structure or content of the original source collection. This makes it easy for organizations to meet compliance standards in regulated industries. The permissions granted to the view are separate from those granted to the underlying views or collections. This greatly reduces the risk of data breaches.ĭBAs can also define aggregate views based on multiple collections or multiple existing views. For example, a view can exclude sensitive data fields, such as personal identifiable informatio n (PII), from sales data and health records.

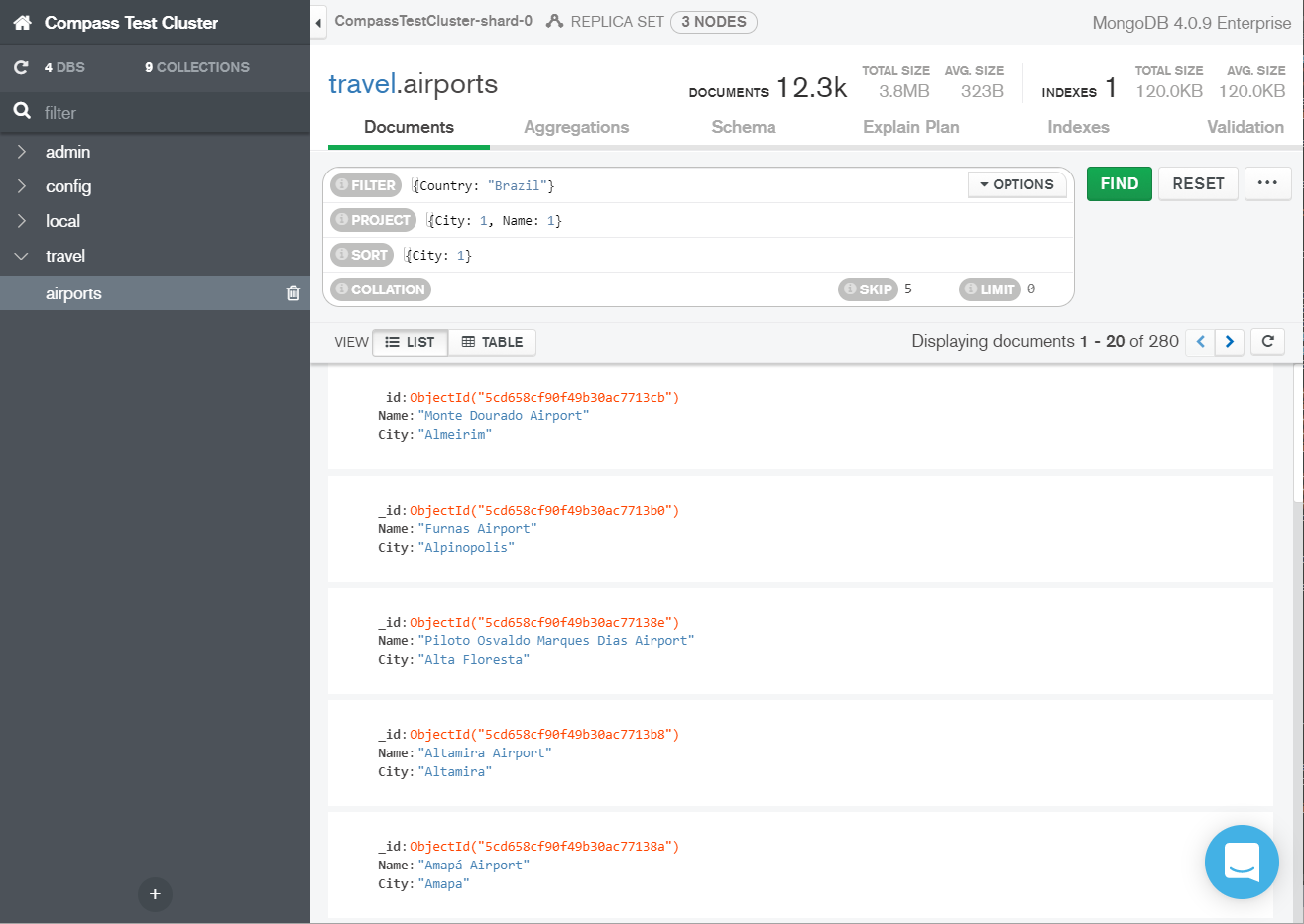
Unlike traditional relational database management systems (RDBMS), MongoDB uses collections and documents instead of tables and rows. MongoDB is a document-oriented NoSQL database that can store large amounts of data.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
